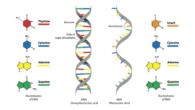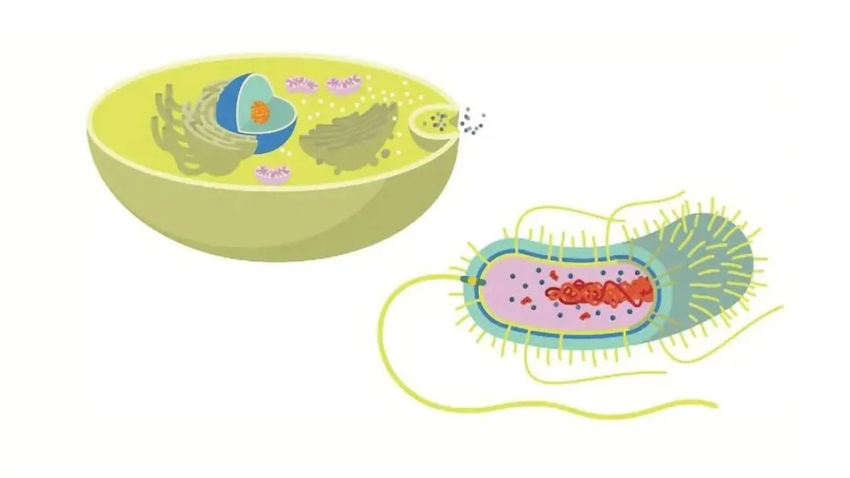
What’s the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
The two basic groups of living things are eukaryotes and prokaryotes. An organism’s group membership is shown by its cell composition. This page will go into some detail on the definitions and distinctions between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
On Definition of Prokaryote
The single-celled organisms known as prokaryotes lack membrane-bound structures.The nucleus is the most important example of this. Most bacterium cells are simple, small, and range in width from 0.1 to 5 μm.
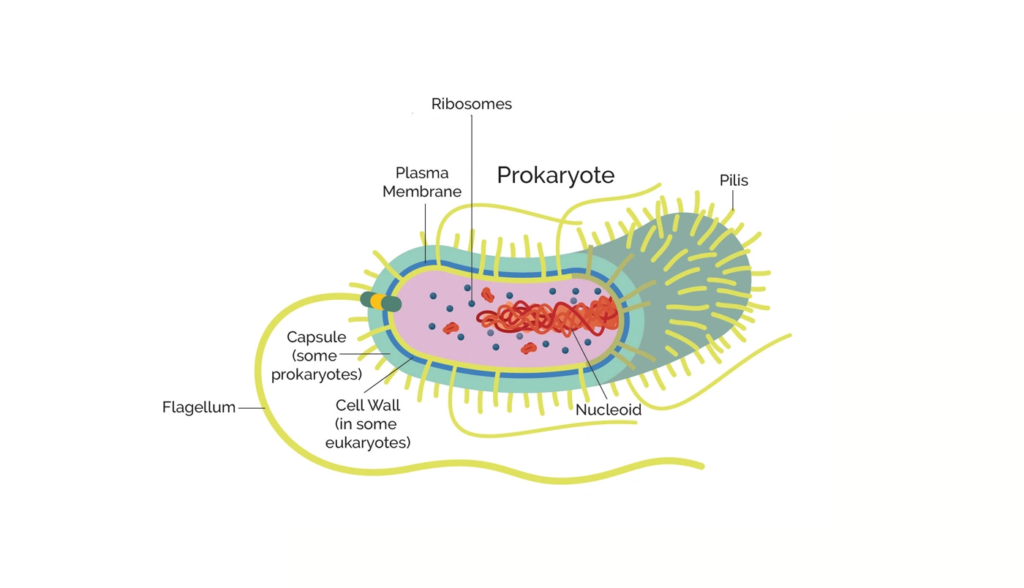
The fundamental components of a prokaryotic cell
Essential components of a prokaryotic cell. With thanks to Technology Networks
While they lack membrane-joined structures, prokaryotic cells do have distinct cell components. The nucleoid is the part of prokaryotic cells where DNA binds together. Bacteria and archaea are the two main groups of prokaryotes. It is possible to find units of protein, DNA, and metabolites all together in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Basic organelles, which are found in bacteria, do work as small compartments to give the structure some order.
Features of prokaryotic cells
What you might find in a prokaryotic bacterial cell is broken down below.
- Nucleoid: The nucleoid is the part of the cell in the middle that holds the DNA.
- Ribosome: Production of proteins is done by ribosomes.
- Cell wall: The cell wall gives the cell shape and keeps out the outside world. It is made up of peptidoglycans, which are proteins and carbohydrates. Most bacteria have a hard cell wall.
- Cell membrane: Known by another name, the plasma membrane, the cell membrane of every prokaryote isolates its interior from the outside world.
- Capsule: Covering the cell wall of some bacteria is a coating of carbohydrates called the capsule. By use of the capsule, the bacteria can adhere to items.
- Little, hair-like features called fimbriae help cells stick together.
- Pili: They move and affix DNA among their many other jobs. Pili are constructions fashioned like rods.
- Flagella: Helping cells move, flagella are tiny, tail-like structures.
Prokaryote instances
Below is a breakdown of possible contents in a prokaryotic bacterial cell.
Do prokaryotes have a centre?
You can’t find a centre in a prokaryote. Instead, prokaryote DNA can be found in the nucleoid, which is in the middle and has a clump of DNA that floats freely. Most prokaryotic DNA is found as a single chromosome made up of circular DNA. Also, these living things don’t have any other membrane-bound structures, like the endoplasmic reticulum.
Exist mitochondria in prokaryotes?
It is false since prokaryotes lack mitochondria. All these cells’ mitochondria. Two further membrane-bound components of cells are the nucleus and the Golgi apparatus; we shall go into these in more detail later.
One theory on the evolution of eukaryotic cells holds that mitochondria were once bacterial cells that coexisted with other cells. Evolving over time, these disparate living entities came to cooperate to form a eukaryote.
Enumerate eukaryotes.
Living creatures classified as eukaryotes have plasma membranes around their nuclei and other components. Inside cells, there are structures called organelles that do many things, like making energy and protein.
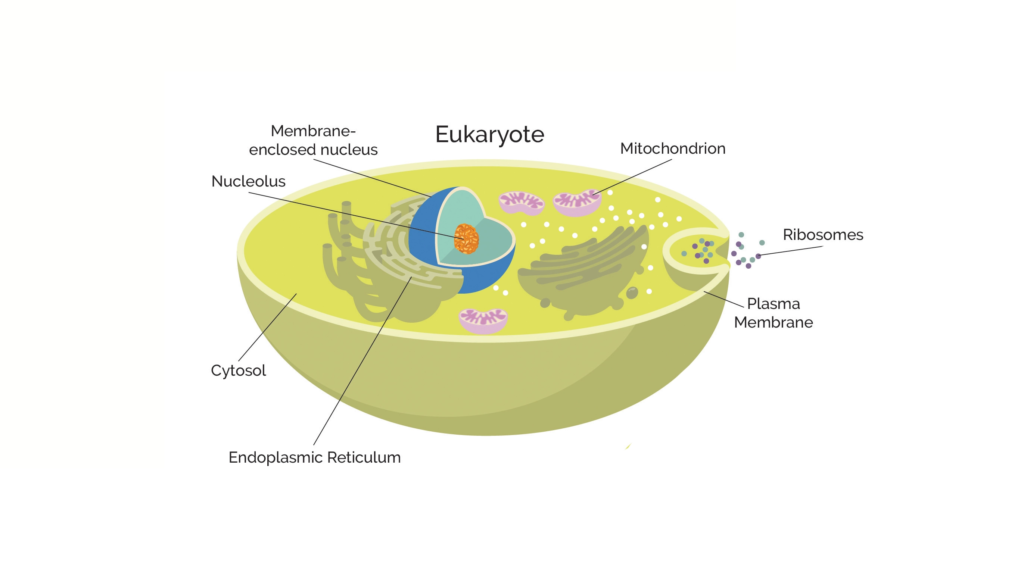
The most important parts of a eukaryotic cell.
The most important parts of a eukaryotic cell. Thanks to Technology Networks
Eukaryotic cells are big (10–100 μm) and have a lot of parts. There are some eukaryotes that only have one cell, but most of them are multiple.
Features of eukaryotic cells
Each membrane-bound structure in a eukaryotic cell does a specific job for the cell. Here is a summary of many of the main parts of eukaryotic cells.
- Nucleus: The genetic stuff is stored in the nucleus as chromatin.
- Node: The nucleolus is the component of live cells that produces ribosomal RNA. Within the nucleus, that is.
- A phospholipid bilayer called the plasma membrane envelops every structure in the cell.
- The cytoskeleton, or cell wall, shapes cells and makes them able to move and divide.
- Overseeing protein production are ribosomes.
- By another term, the “powerhouses” of the cell, mitochondria are the parts of cells that generate energy.
- The cytoplasm is that part of a cell that is between the plasma membrane and the nuclear sheath.
- The organelles are held together by cytosol, a cellular gel-like material.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that helps proteins develop and travel throughout the cell.
- Vesicles and vacuoles: These are membrane-bound sacs that help move things around and store things.
There are also organelles called chloroplasts, lysosomes, and the Golgi apparatus that are found in many eukaryotes but not all of them.
Some examples of eukaryotes
Ecaryotes are made up of animals, plants, mushrooms, algae, and protozoans.
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes side by side
Eukaryotic cells and bacterial cells make up all living things on Earth. They were the first living things. Eukaryotes are thought to have evolved from prokaryotes about 2.7 billion years ago.
One main difference between these two types of living things is that eukaryotic cells have a centre that is enclosed in a membrane, while prokaryotic cells do not. It is in the nucleus that cells store their genetic material. When it comes to prokaryotes, DNA is bundled up in the nucleoid area, but it is not kept in a membrane-bound nucleus.
In eukaryotes, the nucleus is just one of many cells that are inside membranes. On the other hand, prokaryotes don’t have any organelles that are linked by membranes. What makes DNA different is another important thing. The DNA of eukaryotes is made up of many molecules of double-stranded linear DNA, while the DNA of prokaryotes is made up of molecules that are double-stranded and circular.
What prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common
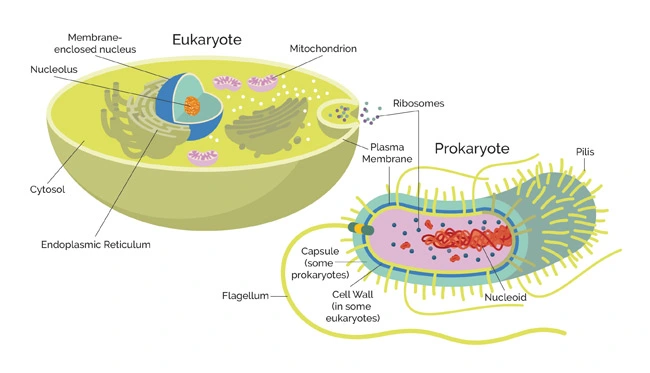
A look at what prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common and what makes them different
A look at what prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common and what makes them different. Thanks to Technology Networks
These four things are true of all cells, whether they are bacterial or eukaryotic:
- DNA
- The plasma membrane
- The cell fluid
- What ribosomes are
How transcription and translation work in prokaryotes and humans
Transcription and translation happen at the same time in bacterial cells, which means that translation starts when mRNA is made.
Transcription and translation are not linked in living cells. mRNA is made during transcription, which happens in the nucleus. After the mRNA leaves the nucleus, translation takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different from each other?
There are several important ways in which prokaryotes and eukaryotes are different. These include structural differences, like whether the cell has a nucleus or not, and chemical differences, like whether the DNA is in a circular or linear shape. The table below shows all of the changes.
| Prokaryote | Eukaryote | |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Cell structure | Unicellular | Mostly multicellular; some unicellular |
| Cell size | Smaller (0.1-5 μm) | Larger (10-100 μm) |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
| DNA Form | Circular | Linear |
| Examples | Bacteria, archaea | Animals, plants, fungi, protists |